With inflation falling, the housing market stabilizing, and consumer spending showing surprising resiliency in the face of rising interest rates, both Wall Street and Main Street are passionately embracing the outlook for an economic soft landing.
Despite enthusiastic buying in the stock market of late, some major recession warning flags have not disappeared, consumer financial stress is increasing, and the Federal Reserve has just increased short-term interest rates by another 0.25% to 5.25%, and signaled that they may not be done raising interest rates.
The question on everyone’s mind: is a recession looming?
To answer that question, with help and data from InvesTech Research, let’s look at both sides: the economic “soft-landing” camp and the “hard-landing” camp, and see if we can’t draw any conclusions using a weight-of-evidence approach.
Evidence Supporting a Soft Landing
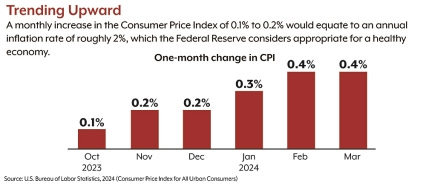
Inflation is Coming Down: The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is leading the optimistic charge in the media, with reports of decreasing inflation over the last twelve months. Headline CPI fell from 4.0% to 3.0% in June on a year-over-year basis. While much of this decline was driven by cyclical factors like energy costs, it still increases the odds of a soft landing.
Contributing to the decrease in overall prices are both the manufacturing and services sectors. The services sector saw inflationary pressures subside starting in early 2022. The Institute for Supply Management Services Prices Paid Index has declined by 30.4 points from its all-time high in December 2021. It has been down for the last seven out of eight months and remains in expansion territory (for now). This, too, supports a possible soft landing.
With decreasing inflation comes decreasing inflation psychology. Recently, consumers have reduced their expectations of inflation over the next year significantly. This measure fell in June to 3.3%, its largest decline since 2008, while the longer-term 5-year expectations remain more firmly anchored at 3.0%.
Actual inflation partially depends on what consumers expect it to be. If consumers expect inflation to be lower next year, businesses will plan to price their goods or services accordingly. It’s likely that the expected inflation rate will continue its downtrend and make a soft landing more likely.
Parts of the economy remain surprisingly resilient: In addition to easing inflation pressures, persistent strength in parts of the economy also supports a potential soft landing. Specifically, the service sector appears to remain resilient.
Services: The Institute for Supply Management Services Index (Non-Manufacturing) remains solidly in expansion territory with a reading of 53.9 last month (any reading above 50 is considered expansionary) and only one month of contraction in the last decade (outside of the pandemic). With services accounting for over 75% of U.S. gross domestic product (GDP), the current Index levels show continued growth. While there is no guarantee this will be maintained, its recent strength provides recession-free hope.
Labor: The relentlessly tight labor market has remained a stronghold of the economy for the last few years. June’s Non-Farm Payrolls report showed 209,000 new jobs created, another banner month for this indicator. The monthly average of new jobs added since January 2022 is almost twice as high as it was during the same period in 2018-2019 prior to the pandemic. In addition, the unemployment rate is currently at 3.6%, just fractionally above its 50-year low. With job growth holding up so well, it doesn’t point to a recession, despite being a heavily revised figure.
Housing: The last bit of soft-landing evidence is one of its strongest – New Home Sales. Sales of new construction have rebounded sharply. New homes currently account for a near-record 29% of all homes for sale, while the historical average is less than half that at just 13%. This recent rebound is driven by a resurgence in enthusiastic buyer psychology, reflected in a rise in traffic of prospective buyers and a reluctance by existing homeowners to sell their homes because of: 1) their current ultra-low mortgage interest rates, 2) higher home replacement costs and 3) potential capital gains taxes on highly appreciated primary residences. Whether this increase is sustainable will be clearer in the coming months.
Evidence Supporting a Hard Landing
A recession may nonetheless be in the cards: While I’ve laid out the evidence in support of a soft landing, many significant indicators just don’t add up, and therefore a recession may still be in the cards.
Leading Economic Index (LEI): The most glaring evidence against a soft landing is the Conference Board’s LEI, which has fallen for 15 consecutive months. Declines of this magnitude have always corresponded to a hard landing, and when the LEI falls below its 18-month moving average, a recession almost invariably follows. Additionally, the LEI’s 6-month rate of change (ROC) is deeply negative, further solidifying this warning flag (red flags are when the 6-month ROC breaks through the zero level prior to a recession). The LEI is historically a reliable indicator, and it is not sending an optimistic signal.
Yield Spreads: Another indicator that is screaming hard landing is the Federal Reserve’s Yield Spread model, which measures the risk of recession in the next 12 months. It’s based on the difference between long-term and short-term Treasury bond yields and recently hit a 42-year high of 71% before retreating slightly to 67% in June. This highly dependable indicator has never reached this level without a resulting recession, although lead times can vary significantly.
Consumer Spending: Lastly, consumer spending has supported the economy for much of the last few years, bolstered by trillions of dollars in stimulus payments and other benefits. Excess savings and lockdowns have helped fuel this strength, though it may be starting to slow.
Within retail sales, “Same-Store Sales” measures growth in revenue from existing (not new) store locations. Johnson Redbook’s latest Same-Store Sales year-over-year figure went negative, indicating fewer purchases compared to a year ago. If this continues to deteriorate, it implies consumers are spending less overall than before, and a recession becomes more probable.
The Federal Reserve’s (a.k.a. The Fed) job is far from over: A potential soft landing combined with some weak economic indicators is a conundrum that puts the Fed in a tight spot. In addition, while headed in the right direction, inflation is still well above the Fed’s 2% target.
Sticky inflation, which tracks items that change in price very slowly, has not come down as rapidly as overall measures. Sticky Price CPI from the Atlanta Fed has started to decline on a 12-month ROC basis but is still quite elevated, with the current reading at 5.8%.
The shorter, 3-month annualized ROC is much lower but still not close enough to the Fed’s target. It’s very likely that Sticky CPI will continue to decline, but the elusive 2.0% will take much longer to reach than the Fed would like.
Core PCE: Yet another, perhaps more important, inflation indicator is the Core Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) Price Index, which measures PCE excluding food and energy. This is the Fed’s preferred measure of inflation and remains at more than twice of the 2.0% inflation target. On Friday, the latest PCE measure came in at 4.1% YoY for June, declining from 4.6% in May.
Making the situation even worse, Core PCE has been flat for the past year and is falling very slowly. Even if it does start to trend lower, it will take quite a long time to reach the target level, putting pressure on the Fed to keep interest rates higher for longer.
Wage Growth: When it comes to inflation, one of the stickiest components is wage growth. The labor market remains tight, there are still more job openings than available employees, and wages continue to rise. The Atlanta Fed’s Wage Growth Tracker is off its all-time high, but at 5.6%, it is still far above its historical average. While increasing wages are beneficial for consumers, it’s a problem for the Fed as failure to control wage growth could risk another inflation surge.
Consumer Distress as a Potential Systemic Risk: Consumers amassed over $2 trillion in excess savings after the pandemic, primarily due to government support and lockdowns. This backlog of cash has helped smooth over many underlying problems in the economy. After lockdowns ended, consumers spent as if they had unlimited funds. Tack on a decades-high level of inflation, and they’ve now burned through over 80% of their excess savings. Based on current trends, these savings will be completely exhausted by the end of this year. Once savings are depleted, some consumers will likely resort to what is now very expensive revolving debt.
And some already have. Despite the amassed excess savings in some households, consumers still took on more debt than ever after the pandemic. As a result, the combination of auto loans, credit card debt, student loans, and other debt is now at a record high – 72% higher than during the Great Financial Crisis.
Regarding student loan debt, the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau reported that half of borrowers whose payments are scheduled to restart soon have other debts that are at least 10% more expensive now than before the pandemic. If these trends persist, consumers may struggle to bring their savings back to pre-pandemic levels.
Those who have opened new credit cards in recent years or regularly carry credit card debt are quickly coming under more severe financial stress. Monetary tightening has driven average credit card interest rates to over 22% in May – the highest rate since the Federal Reserve began tracking the data in late 1994. Extremely high credit card interest rates combined with record consumer debt outstanding could prove to be an ominous combination.
Consumer spending is the ultimate driver of the economy, making up almost 70% of GDP. If consumers can no longer afford to spend, this systemic risk can become a reality.
The Weight of Evidence
While the evidence is compelling in both the economic soft-landing and the hard-landing camps, more upcoming near-term economic data will help tip the scale solidly into one of the camps.
While it’s easy to say that a recession is inevitable, one could make that statement anytime during our lifetimes. Indeed, it’s not a matter of whether we’ll have a recession because we will. It’s all about the “when” of the recession.
In my opinion, the weight of current evidence supports a recession starting within six months. To be honest, I personally thought we were already in a recession, but the economic data has not supported that opinion, which means I have been wrong so far.
Regardless, a continued deterioration in consumer spending, increasing debt levels, growing layoffs, and higher short-term interest rates will have a detrimental impact on consumer confidence, which constitutes a negative feedback loop that will lead to even further reduced consumer spending and increasing layoffs.
The next few months will be very revealing…. if not exciting!
If you would like to review your current investment portfolio or discuss any other financial planning matters, please don’t hesitate to contact us or visit our website at http://www.ydfs.com. We are a fee-only fiduciary financial planning firm that always puts your interests first. If you are not a client, an initial consultation is complimentary and there is never any pressure or hidden sales pitch. We start with a specific assessment of your personal situation. There is no rush and no cookie-cutter approach. Each client is different, and so are your financial plan and investment objectives.
Source: Investech Research