Economic reports of late seem to point to a weakening economy and stubborn inflation.
On April 30, the Employment Cost Index for the first calendar quarter of 2024 showed a 1.2% increase (4.2% year-over-year); that was 25% higher than the consensus estimate of 0.9%.
The FHFA House Price Index for February 2024 was much hotter than expected, coming in at 1.2% versus 0.1% expected (7.0% year-over-year.) Similarly, the February Case-Shiller 20-City Home Price Index came in at 0.6% versus 0.1% expected (7.3% year-over-year.)
At the same time, two more economic reports were released on April 30.
The Chicago Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) was 37.9 (versus 45 expected).
The Conference Board’s Consumer Confidence Index also came in far below expectations (97 versus 104 expected).
The stock markets were understandably confused: Normally, lower economic activity means lower inflation. Instead, what we got was higher inflation and lower economic activity.
In the stock markets, confusion equals selling now and asking questions later. That’s what we are seeing now.
Persistent Inflation
On April 10, 2024, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics released the Consumer Price Index (CPI) for March, and the increase in CPI — the most commonly cited measure of inflation — was higher than expected. The rate for all items (headline inflation) was 3.5% over the previous year, while the “core CPI” rate, which strips out volatile food and energy prices, was even higher at 3.8%. The month-over-month change was also higher than anticipated at 0.4%. (1)
The stock market then dropped sharply on this news and continued to slide over the following days, while economists engaged in public handwringing over why their projections had been wrong and what the higher numbers might mean for the future path of interest rates. Most projections were off by just 0.1% — core CPI was expected to increase by 3.7% instead of 3.8% — which hardly seems earth-shattering to the casual observer. But this small difference suggested that inflation was proving more resistant to the Federal Reserve’s high interest-rate regimen (raising interest rates is one of the most common ways to curb spending and corporate investing to reduce inflationary pressures.) (2)
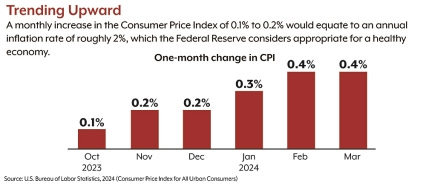
It’s important to remember that the most dangerous battle against inflation seems to have been won. CPI inflation peaked at 9.1% in June 2022, and there were fears of runaway inflation similar to the 1980s. That did not happen; inflation declined steadily through the end of 2023. The issue now is that there has been upward movement during the first three months of 2024.(3) This is best seen by looking at the monthly rates, which capture the current situation better than the 12-month rates. March 2024 was the third increase month that points to higher inflation (see chart).
High for longer
While price increases hit consumers directly in the pocketbook, the stock market reacted primarily to what stubborn inflation might mean for the benchmark federal funds rate and U.S. businesses. From March 2022 to July 2023, the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC or AKA the Fed) raised the funds rate from near-zero to the current range of 5.25%–5.5% to slow the economy and hold back inflation.
At the end of 2023, with inflation moving firmly toward the Fed’s target of 2%, the FOMC projected three quarter-percentage point decreases in 2024, and some observers expected the first decrease might be this spring. Now it’s clear that the Fed will have to wait to reduce rates. (4)(5)
Higher interest rates make it more expensive for businesses and consumers to borrow. For businesses, this can hold back expansion and cut into profits when revenue is used to service debt. This is especially difficult for smaller companies, which often depend on debt to grow and sustain operations. Tech companies and banks are also sensitive to high rates. (6)
As mentioned above, in theory, high interest rates should hold back consumer spending and help reduce prices by suppressing demand. So far, however, consumer spending has remained strong. In March 2024, personal consumption expenditures — the standard measure of consumer spending — rose at an unusually strong monthly rate of 0.8% in current dollars or 0.5% when adjusted for inflation. (7)
The job market has also stayed strong, with unemployment below 4% for 26 consecutive months and wages rising steadily. (8)
The fear of keeping interest rates too high for too long is that it could slow the economy, but that is not the case, making it difficult for the Fed to justify rate cuts.
What’s driving inflation?
The Consumer Price Index measures price changes in a fixed market basket of goods and services, and some inputs are weighted more heavily than others.
The cost of shelter is the largest single category, accounting for about 36% of the index and almost 38% of the March increase in CPI. (9) The good news is that measurements of shelter costs — primarily actual rent and estimated rent that homeowners might receive if they rented their homes — tend to lag current price changes, and other measures suggest that rents are leveling or going down. (10)
Two lesser components contributed well above their weight. Gas prices, which are always volatile, comprised only 3.3% of the index but accounted for 15% of the overall increase in CPI. Motor vehicle insurance prices comprised just 2.5% of the index but accounted for more than 18% of the increase. Together, shelter, gasoline, and motor vehicle insurance drove 70% of March CPI inflation. On the positive side, food prices comprised 13.5% of the index and rose by only 0.1%, effectively reducing inflation. (11)
While the Fed pays close attention to the CPI, its preferred inflation measure is the personal consumption expenditures (PCE) price index, which places less emphasis on shelter costs, includes a broader range of inputs, and accounts for changes in consumer behavior. Due to these factors, PCE inflation tends to run lower than CPI. The annual increase in March was 2.7% for all items and 2.8% for core PCE, excluding food and energy. The monthly increase was 0.3% for both measures. (12)
Although these figures are closer to the Fed’s 2% target, they are not low enough, given strong employment and consumer spending, to suggest that the Fed will reduce interest rates anytime soon. It’s also unlikely that the Fed will raise rates.
The Fed seems poised to give current interest rates more time to push inflation to a healthy level, ideally without slowing economic activity. (13)
And since higher interest rates mean more competition for investment dollars and lower corporate earnings, stock markets don’t tend to react favorably, especially when 3-4 interest rate cuts were expected earlier this year.
The Fed issues its next interest rate decision on Wednesday afternoon, May 1, 2024. No change in interest rates is all but a given. However, what Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell says about the recent economic data and the Fed’s stance on when future rate cuts are coming will no doubt be parsed word for word for clues when the press conference is convened.
Please pass the popcorn.
If you would like to review your current investment portfolio or discuss any other retirement, tax, or financial planning matters, please don’t hesitate to contact us at 734-447-5305 or visit our website at http://www.ydfs.com. We are a fee-only fiduciary financial planning firm that always puts your interests first. If you are not a client, an initial consultation is complimentary, and there is never any pressure or hidden sales pitch. We start with a specific assessment of your personal situation. There is no rush and no cookie-cutter approach. Each client and your financial plan and investment objectives are different.
Footnotes:
1, 3, 8–9, 11) U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, 2024
2)The New York Times, April 10, 2024
4) Federal Reserve, 2023
5) Forbes, December 5, 2023
6) The Wall Street Journal, April 15, 2024
7, 12) U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis, 2024
10) NPR, April 18, 2024
13) Bloomberg, April 19, 2024